Industrial-Grade Animal Fat Primary Rendering
Explore More-
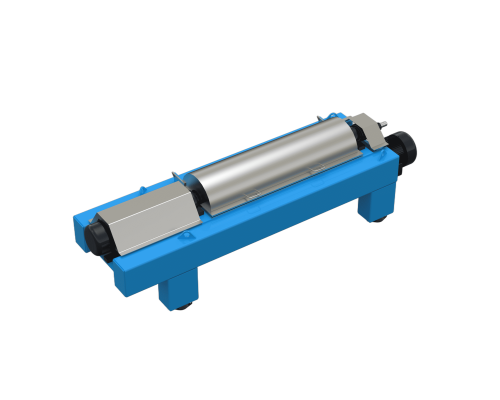
Centrifuge
-
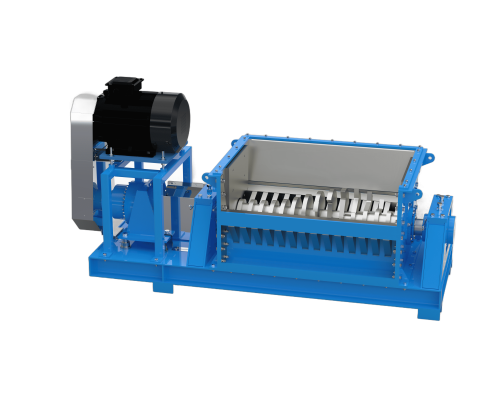
Feed Grade Crusher
-
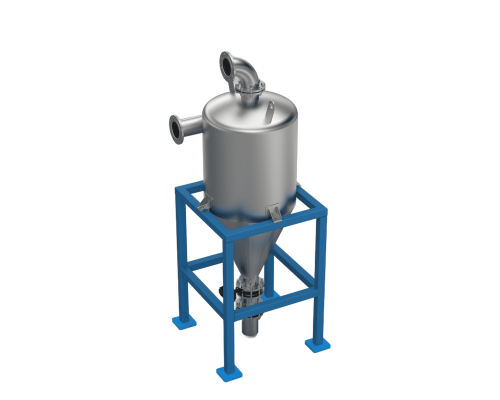
Cyclone
-
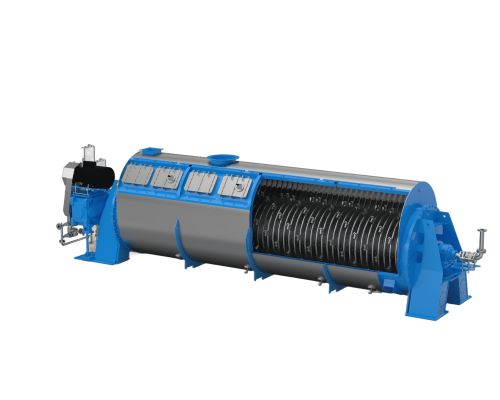
Disc Dryer
-
Fat Filtrator
-
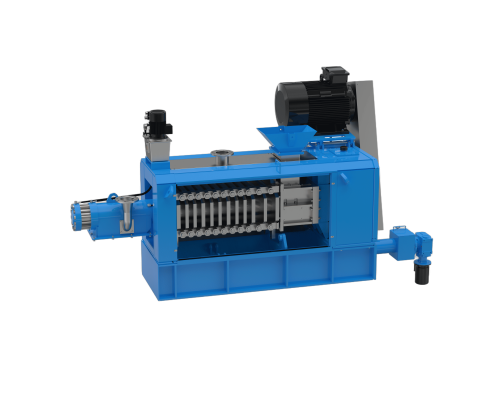
Fat Press
-
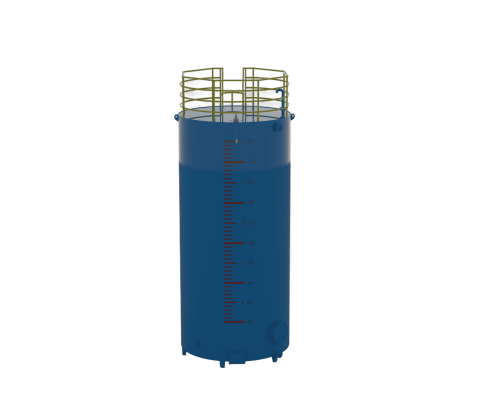
Finished Oil Storage Tank
-
Material Bin
-
Milling Plant
-
Meal Cooling
-
Scrubber
-
Oil Pump
-
Condenser
-
Heating Buffer Tank
-
Meat Scraps Storage Bin
Food-Grade Animal Fat Primary Rendering
Explore More